Omicron transmission: how contagious diseases spread
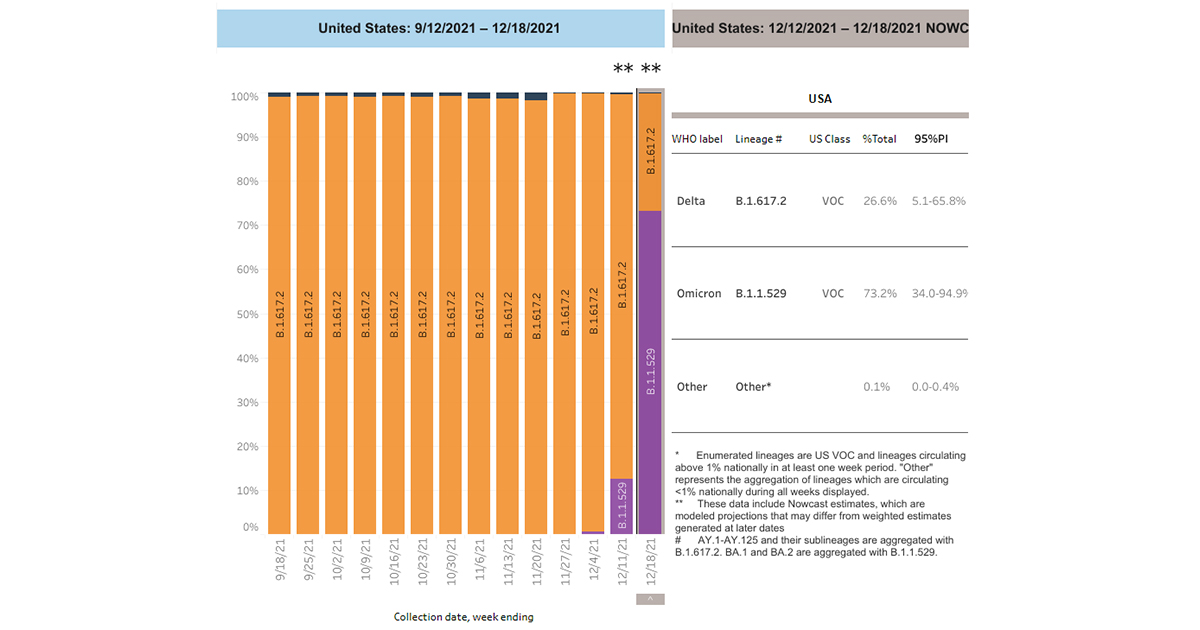
As of December 2021, community transmission is high or substantial in over 90% of U.S. counties. That includes Douglas and Sarpy counties.
Locally, our hospitals are overwhelmed with COVID-19 patients, which affects how many patients we can treat for other diseases. Omicron appears to be even more transmissible than the delta variant, which will put further strain on our health care workers.
What is R? Measuring contagious diseases
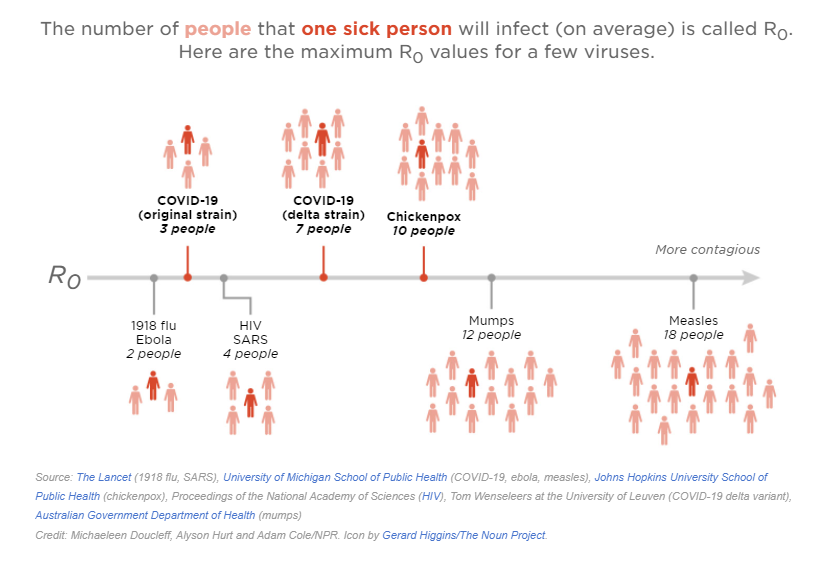
Researchers measure disease transmission with R, the "effective reproductive number." R is the answer to the question of: "How many people does one sick person infect, on average?"
For example, an R of 2 means that each sick person infects two new people, on average.
Maximum R estimates in an unprotected population (no vaccines, masks or other proven methods of prevention):
- 1918 flu: 2
- Ebola: 2
- SARS: 4
- Smallpox: 7
- Polio: 7
- Mumps: 12
- Measles: 18
You can help slow the spread of highly infectious diseases like omicron
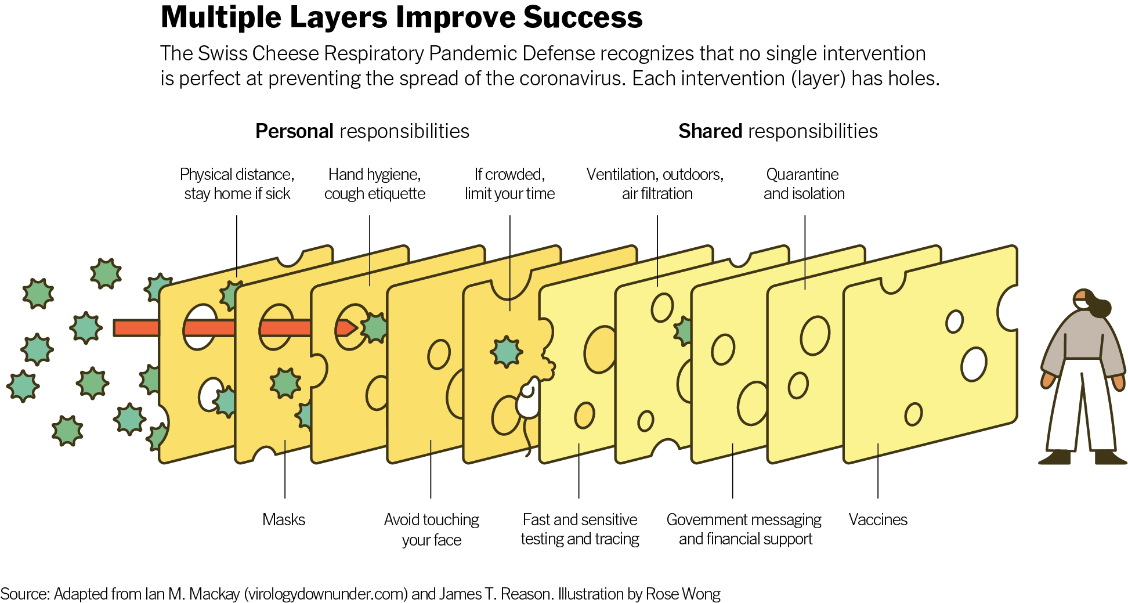
R can be reduced with these proven methods:
- Increase resistance of potential hosts. Meaning, get vaccinated and get your booster.
- Reduce viral shedding. Meaning, wear masks.
- Prevent contact with virus. Meaning, isolate if you're sick. If you have any COVID-19 symptoms, get tested immediately. If you've had contact with someone who has COVID-19, follow quarantine guidelines.
- Reduce exposure of susceptible people. Meaning, wear masks. Choose outside over indoors. Postpone gatherings if community transmission is high (nearly everywhere in the U.S.). Practice physical distancing.
How contagious is omicron?
We don't know yet. Omicron's effective transmission, or R, will also vary from place to place (see "How are infectious diseases spread?" below).
"Delta appeared to be twice as transmissible as previous SARS-CoV-2 viruses," says infectious diseases expert James Lawler, MD, MPH. "Estimates for omicron have ranged up to four times as transmissible as delta, but most estimates range from 1.5 to 2 times."
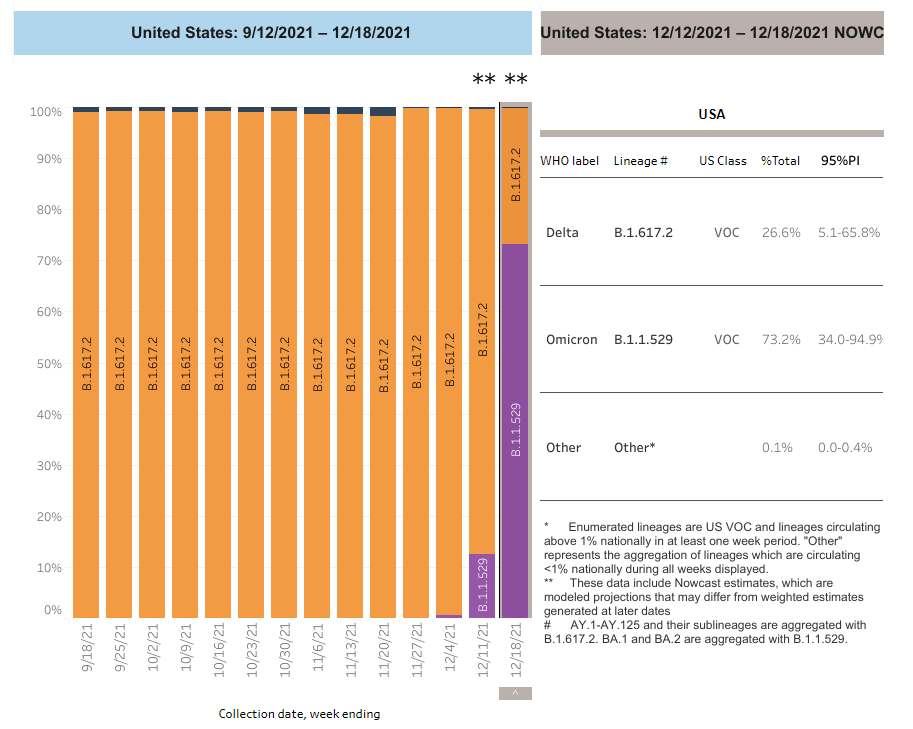
In just two weeks, omicron has become the dominant variant in the United States. In the week ending Dec. 4, omicron was an estimated less than 1% of positive cases.
Omicron now makes up 73% of positive COVID-19 tests, compared to delta's 27% of positive tests nationwide.
How are infectious diseases spread?
R depends on:
- Immune resistance. Vaccines and prior infections often have a protective benefit against a disease. In the case of COVID-19, vaccination is more durable than disease-acquired immunity
- Transmission method. Different diseases spread in different ways. Ebola spreads through bodily fluids like blood or vomit. Measles and COVID-19 spread through the air through respiratory droplets
- Where you live. Epidemiology is local. Death rates from COVID-19 depend on where you live, because every country, state, county and community have responded differently. In fact, individual counties in the U.S. have wildly different COVID-19 death rates that are linked to political polarization
- The number of infectious particles needed to make someone sick. Some viruses require a lot of viral particles to transfer from a sick person to a new person for the new person to get sick. The amount of time you spend with a sick person affects how many viral particles you're exposed to. Properly-worn masks and good ventilation reduce the number of viral particles transferred from person to person
- Human behavior. If individuals wear masks, choose to get vaccinated and boosted, socially distance and choose small gatherings that are outdoors or in well-ventilated settings, they can decrease the effective R of the disease in their area
Illustrating R with a magic penny
A business partner offers you either a magic penny or a million dollars. Every day the penny's value doubles. Being wise and fiscally savvy, you choose the magic penny.
- Day 1: $0.01
- Day 2: $0.02
- Day 3: $0.04
- Day 4: $0.08
Let's skip ahead to day 10. Now you have $5.12. Day 15 brings you $163.84. And day 20? $5,242.88.
By day 30, your magic penny has become $5,368,709.12 – far greater than the offer of a million dollars.
This is the power of exponential growth.
A penny that doubles is like an R value of two. Remember that the 1918 flu had a maximum R value of two, and that pandemic killed at least 50 million people around the world.
Fast transmission (large R) can quickly overwhelm hospital capacity
If the R of a disease is greater than one, the number of infected people grows over time. Large gatherings indoors with unmasked people can accelerate disease transmission.
If the R of a disease is less than one, the number of infected people shrinks over time. Masks, vaccines and other public health measures slow the spread of a disease.
The higher R is, the faster a disease can spread. But we can slow down a disease's transmission (decrease R) with proven practices.
Omicron could be up to four times more transmissible than delta – that will devastate our health care system if we don't slow it down. Get vaccinated. Get boosted. Wear a mask.